WSF_AIR_MOVER¶
- mover WSF_AIR_MOVER¶
mover WSF_AIR_MOVER Platform Part Commands // Mover Commands update_interval update_time_tolerance // Route Mover Commands altitude_offset at_end_of_path draw_route on_turn_failure pathfinder print_route start_at start_time switch_on_approach switch_on_passing turn_failure_threshold use_route // Waypoint Mover Commands angle_of_attack_table altitude speed angle bank_angle_limit body_g_limit heading_pursuit_gain maximum_climb_rate maximum_flight_path_angle maximum_linear_acceleration maximum_radial_acceleration maximum_altitude minimum_altitude maximum_speed minimum_speed path_variance_radius roll_rate_limit speed_variance_percent turn_rate_limit pitch_disable no_pitch on_road off_road path_compute_timestep // Air Mover Commands maximum_impact_speed end_mover
Overview¶
WSF_AIR_MOVER is a Route Mover designed for simplified air vehicle motion. The advantage of using the WSF_AIR_MOVER is that a platform’s mass properties, aero, or propulsion is not required to be known to model an air body. Movement is based on maximum limits set for items (e.g., linear acceleration, velocity, Gs, radial acceleration), but it applies only to the continuous motion in the horizontal plane. The limitation of the WSF_AIR_MOVER is within the vertical transitions (altitude changes) of the platform. These transitions are discontinuous in that the effects are instantaneous because transitional vertical pitch rates and vertical accelerations are not modeled. If continuous and smooth vertical and horizontal transitions are desired on a platform, use the WSF_KINEMATIC_MOVER (if no aerodynamics, mass properties, propulsion, or altitude effects are desired) or the WSF_P6DOF_MOVER (if realistic, physics-based modeling is desired).
Mover Commands¶
- update_interval <time-value>¶
If non-zero, specifies a periodic time interval at which the simulation will call the mover. If zero then the mover will be called only when it is necessary to determine the position of the containing platform.
Default: 0 seconds unless overridden by the specific mover implementation.
- update_time_tolerance <time-value>¶
When a position update is requested by the simulation, if the time since the previous update is less than or equal to this value then the mover will ignore the update.
Default: Most mover implementations define this as the time it takes to travel 1 meter at some nominal velocity that is appropriate for the implementation.
Note
A mover implementation may choose to ignore this command.
Route Mover Commands¶
- altitude_offset <length-value>¶
When set, this offset will offset the parent platform’s location by the given amount from the current waypoint’s altitude.
- at_end_of_path [extrapolate | stop | remove]¶
Specify the action to take when the mover reaches the end of its defined path.
extrapolate: continue moving along at the last known heading, speed, and altitude.
stop: stop moving, but leave the platform in the simulation.
remove: remove the platform from the simulation.
Default Extrapolate
- draw_route <boolean-value>¶
This command is the same as print_route, except the route text is not printed, only drawn with WsfDraw.
- on_turn_failure [best_effort | reverse_turn | ignore_point]¶
Defines the behavior of the mover when a point on a route cannot be reached exactly due to the turn radius.
- best_effort:
Turns until the platform reaches the point of closest approach to the point.
- ignore_point:
The mover operates effectively as if the point is not there. Any script tied to this point will be executed when the point is skipped.
- reverse_turn:
The mover will turn the opposite direction, enabling it to reach the point exactly.
Note
This command has no effect if the mover is given routes that fit within the mover’s constraints
Note
Also see turn_failure_threshold.
Default best_effort
- pathfinder <path-name>¶
The name of the pathfinder object to use.
- print_route <boolean-value>¶
When enabled, the route is printed to the screen whenever it is modified. Additionally, WsfDraw is used to output a visual of the route, which can be viewed with many visualization tools.
- start_at <label-name>¶
The label identifying the waypoint in the route to use as the starting location.
- start_time <random-time-reference>¶
Indicates the platform is to start moving at the time specified. The current velocity is set to zero and once the simulation time is reached, the platform starts moving at the speed specified in the first waypoint. If an elapse time is desired at a waypoint, use the subcommand pause_time.
- switch_on_approach¶
Switches to the next waypoint when approaching within one turn radius of the current target waypoint.
- switch_on_passing¶
Switches to the next waypoint only when abreast of the current target waypoint.
Note
This is the default.
- turn_failure_threshold <ratio-value>¶
Defines the threshold for which the on_turn_failure behavior is triggered, given as a ratio of the turn radius. For example, a turn_failure_threshold of 0.01 and a turn radius of 1000 meters, on_turn_failure logic would be triggered if the point is missed by more than 10 meters.
Default 0.01
- use_route <route-name>¶
Supplies the name of the route to follow. The route is assumed to be a predefined absolute route.
Waypoint Mover Commands¶
- angle_of_attack_table … end_angle_of_attack_table¶
- angle_of_attack_table
end_angle_of_attack_table
- altitude <altitude-value>¶
Specifies the altitude that the subsequent data is valid for. The altitude blocks must be in increasing numerical order. Linear interpolation of the altitude blocks is used.
- speed <speed-value>¶
Specifies the speed that the listed angle of attack is valid for. The speed entries must be in increasing numerical order. The angle of attack will be computed using a linear interpolation of the speed data.
- angle <angle-value>¶
The angle of attack. The angle of attack entries must be in increasing numerical order.
- bank_angle_limit <angle-value>¶
The roll angle limit. Value must be between 0 degrees to 85 degrees. Used to calculate the maximum radial acceleration.
Default 0
- body_g_limit <acceleration-value>¶
The body g-limit. Value must be greater than the acceleration of earth’s gravity.
- heading_pursuit_gain <double-value>¶
The heading pursuit gain.
Default 5
- maximum_climb_rate <speed-value>¶
Specifies the maximum climb rate and dive rate used when changing altitude. Other climb rates specified by waypoints or scripts are bounded by this value.
Note
The actual climb rate of the mover will also be affected by ‘maximum_flight_path_angle’
- maximum_flight_path_angle <angle-value>¶
Specifies maximum flight path angle (angle of climb/dive). Value must be greater than or equal to 0.
Note
The actual climb rate of the mover will also be affected by ‘maximum_climb_rate’
Default 0
- maximum_linear_acceleration <acceleration-value>¶
Specifies the maximum linear acceleration to use when acceleration is necessary. This value is used if the waypoint does not include a linear _acceleration specification.
Default 6 g’s
- maximum_radial_acceleration <acceleration-value>¶
Specifies the maximum radial acceleration to use when turning. This value is used if the waypoint does not include a radial_acceleration specification.
Default 6 g’s
- Note:
The radial acceleration is NOT the load factor for the aircraft. For example, if one desires a maximum load factor of n = 2 for a 2g turn, then the radial acceleration for a desired 2g turn limit would need to be set =
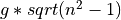 = 1.732g.
= 1.732g.
- maximum_altitude <altitude-value>¶
Maximum altitude constraint.
- minimum_altitude <altitude-value>¶
Minimum altitude constraint.
- maximum_speed <speed-value>¶
Maximum speed constraint. Value must be greater than 0.
- minimum_speed <speed-value>¶
Minimum speed constraint. Value must be greater than or equal to 0.
Default 0.0
- path_variance_radius <length-value>¶
This value will randomly vary the location of the waypoint within the radius given. A random bearing and distance are chosen and applied to the next waypoint when calculating the path.
- roll_rate_limit <angle-rate-value>¶
The roll rate limit. Value must be greater than 0. Note: When applied to a WSF_AIR_MOVER or other waypoint mover types, the roll rate will not affect the platform’s movement along a route. To affect route following behavior use maximum_radial_acceleration.
- speed_variance_percent <percent-value>¶
This value will randomly vary the speed at each waypoint as the mover travels within +/- the pct given. Value must be greater than 0.
- turn_rate_limit <angle-rate-value>¶
The turn rate limit. Value must be greater than 0.
- pitch_disable¶
- no_pitch¶
Restricts the mover from pitching the platform. This has no effect on kinematics.
- on_road¶
Restricts the mover from rolling the platform. This has no effect on kinematics.
- off_road¶
Turns off the ‘on_road’ option. This allows the platform to roll.
- path_compute_timestep <time-value>¶
Waypoint movers precompute movement along paths. This behavior forces turns to have a constant radius. If path_compute_timestep is specified as a positive value, the turn rate will update on that interval if any changes in speed occur.
Default 0.0
Note about maximum and default commands¶
Movers have various commands that specify a maximum value such as maximum_linear_acceleration. These commands
specify an overall limit to movement which will not be exceeded over the course of a simulation. There are a few
default commands, such as default_linear_acceleration. These commands specify a rate to use unless otherwise specified
in a route or script. These parameters may be omitted, leaving the mover to use the maximum rates by default. Rates
may be modified during the simulation through routes, such as with the
linear_acceleration command, or through scripts, such as the
GoToSpeed() method. Rates remain the same until changed by another script or route. Routes
provide a mechanism to return to a default rate, such as using the linear_acceleration default command.
Air Mover Commands¶
- maximum_impact_speed <speed-value>¶
Specify the maximum speed above which the associated platform intersects terrain and is considered ‘crashed into the ground’. A crashed platform will notify observers via the WsfSimulationObserver::CrashedIntoGround() method and remove itself from the simulation. If impact speed is below this maximum, the platform is considered to be ‘landing’. The default behavior is to always land, rather than crash.

